Have you heard that 40% of American bank customers don’t visit bank offices for six months or more? and that’s all because of the technical progress in the financial or say banking sector.
That said, the banking industry has been facing significant changes since the advent of advanced techs, and one such is better known as Open Banking.
A system that not only strengthens data security but also offers customized services and innovative monetary solutions tailored to both individuals and businesses.
However, that’s not enough, and to know more, you must take an insight into this blog, and explore the fundamentals of open banking and the emerging trends that are reshaping the financial services field.
Open Banking, also called ‘Open Bank Data’ is a banking system where banks and other financial institutions share their customers’ bank data through APIs, driving marketing, personalization, and financial services improvements.
Prior such pieces of information were kept closed, and third parties were not allowed to access the internal data.
Even at the present time, the data cannot be made openly available and is only shared at the explicit request of the customer.
This empowers customers with more control over their monetary data, paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and dynamic financial ecosystem.
APIs play a pivotal role in open banking by facilitating the fast and secure exchange of data between banks and financial institutions.
This system decentralizes traditional banking, shifting data from closed networks to open, interconnected platforms.
When centralized banks often rely on private servers that limit third-party integration, APIs enable external applications to connect effortlessly to financial systems.
This seamless access to data enhances service offerings and fosters greater innovation across the industry.
For some, open banking might seem like a new development, but many applications are already utilizing its platform to enhance various financial services:
The system allows users to make direct payments from their bank accounts online without relying on traditional payment gateways.
This speeds up transactions and reduces costs by cutting out intermediaries.
Financial advisors and account managers can access data from multiple financial sources, providing a holistic view of a client’s economic status.
This enables better-informed decision-making and more strategic investment advice.
The rapid processing capabilities of APIs allow for faster loan evaluations and approvals.
Financial institutions can offer personalized loan terms and interest rates based on an individual’s financial behavior, resulting in more transparent and accurate credit assessments.
Banks can offer tools for managing expenses, tracking spending, and creating personalized budget plans based on user preferences and income.
This includes automating the analysis of recurring payments and expenditures.
Open banking supports customized offerings such as loyalty programs, bonus rewards, and tailored financial advice, which help increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Real-time data analysis through automated systems allows for faster detection of suspicious activity and swift responses to minimize financial risks and safeguard user information.
When decentralized open banking can strengthen user trust, some companies may hesitate to share sensitive data due to competitive concerns.
Have You Heard That?
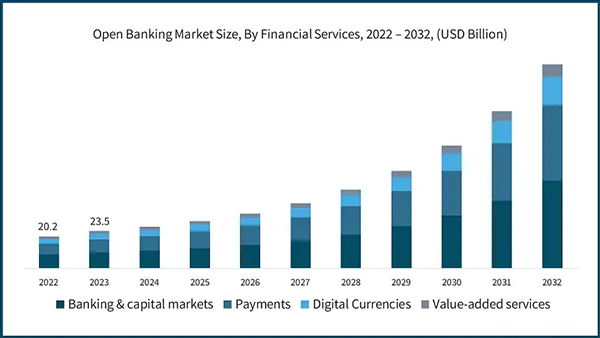
The number of open banking users worldwide is projected to reach 159.3 million by the end of 2024.
Open banking has gained global traction, with various regions implementing regulations to ensure its secure adoption.
In Europe, the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) introduced in 2018 and the updated PSD3 in 2023 have improved payment transparency and security.
The UK adopted the Payment Services Regulations (PSRs) in 2017 and established the Open Banking Implementation Entity in 2018 to oversee its progress.
In the United States, the Financial Data Exchange (FDX) was formed in 2018 to facilitate secure data transfers, with comprehensive regulations anticipated by 2024.
Across Asia, Japan’s 2017 amendments to the Banking Act and South Korea’s full-scale transition to open banking in 2019 have positioned these countries as regional leaders, while Singapore continues to take steps to advance open banking initiatives.
Open banking is modernizing traditional banks by integrating advancements in decentralized finance and improving online financial services.
This transformation is propelled by monetary service providers and technology companies leveraging APIs to access banking data, optimise operations, and create innovative offerings.
Consequently, banks can provide enhanced features like automated loan applications, personalized budgeting tools, financial planning services, and streamlined payment initiation.
Despite concerns surrounding sharing personal and financial data with third parties, governments are establishing strong regulations to safeguard data privacy and ensure the security of API integrations and providers.
