3D printing has dominated the discussion around speedy, affordable manufacturing methods for some time now.
And yet, this dominance has come at the expense of competing processes, meaning that many businesses don’t explore all the options when developing products.
To clear things up, here is an overview of two other approaches you can take, in the form of rapid injection molding and CNC machining, covering what they are, where they make sense to use, and how to choose between them.
To explain in simple words, Injection Molding is a fast-paced, cost-effective process used in manufacturing to produce intricate plastic parts and components.
It’s a technique that leverages automated machines and injection molding tools for the quick creation of prototype models or final products.
The crux of the process involves injecting molten material, typically thermoplastic polymers, into predefined molds under high pressure. This method unfolds swiftly, hence the term ‘rapid’, enabling manufacturers to produce high-quality components in relatively short time frames.
The versatility of rapid injection molding makes it an ideal solution across various industries like automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
For example, car manufacturers frequently use this method to create mundane components such as cupholders, as well as technical parts like electrical connectors.
This process comes with a set of advantages that makes it favorable within the manufacturing sector, just as 3D printing has its perks.
These include:
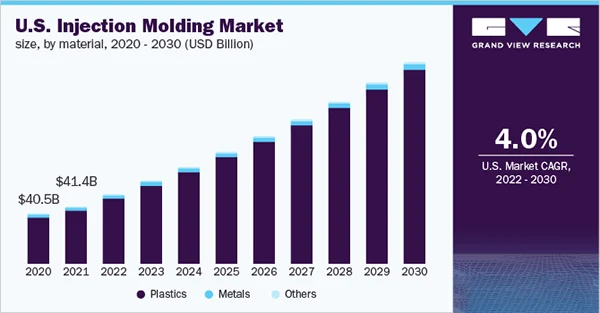
The above graph shows the growth report of the Injection molding market in the US in the future.
Yet like any other technique, this too has its disadvantages:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is another popular manufacturing method, highly revered for its precision and versatility. It involves the automated control of production tools using a programmable computer.
In essence, a digital template instructs the machine tool’s movements, enabling it to sculpt materials into desired shapes with exceptional accuracy.
These machines can perform intricate cutting tasks along three different axes simultaneously, which allows complex parts to be made all in one go.
From metals like steel and aluminum to woods and plastics, CNC machining accommodates a wide range of materials, making it ideal for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, or electronics. For instance, it’s regularly used in medical device production where strict tolerances are vital.
Did You Know?
NASA successfully tested 3D printing in the zero gravity of space, printing a ratchet wrench on the ISS.
As you no doubt have suspected, computerized machines bring plenty to the table in terms of benefits, and just a few of these are:
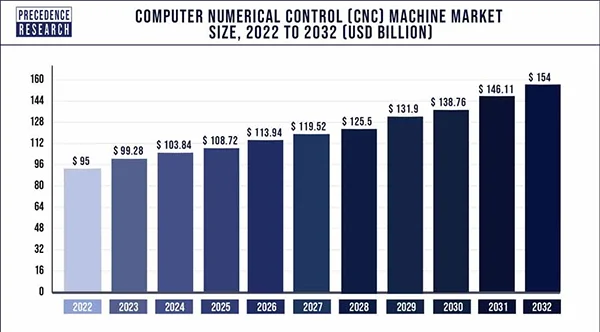
The above statistics show the expected market size of the CNC machine market in the future.
But unfortunately, it’s not without its downsides:
When it comes to selecting a 3D printing alternative between rapid injection molding and CNC machining, there are several elements you need to consider that can affect your final decision:
Of course, these factors aren’t standalone, but rather they interact with one another, so each case demands bespoke evaluation. Neither method is inherently superior but dependent upon project parameters.
So if you seek fast high-volume production or require complex small runs prioritizing precision, you have to pick a route based on your needs.

Alt-tag: Injection molding and CNC machining image
It’s a good idea to evaluate and experiment with several forms of producing, from 3D printing to rapid injection molding and CNC machining, if you have the opportunity.
Even the simple act of examining parts and products produced by other brands using them will give you more insight to drive your own choices.
