JIS L 1920 test method is a Japanese industrial standard testing method for antimicrobial activity and efficacy of textile products. Japanese standards formulated this test to examine the ability of antimicrobial-treated fabrics to inhibit or kill microorganisms. In this test, the technicians examine the material for its antimicrobial property over 18 hours.
Today, in this blog, we will learn everything about JIS L test procedure. So keep on reading till the end.
Antimicrobial agents are functional textile additives and are now more popularly used in many textile industries. They provide resistance against the microbes that cause foul odor and color change in the fabric. With a more active and improved lifestyle, the demand for antimicrobial fabric products has increased to a greater extent.
Various companies are developing antimicrobial and antifungal strains for incorporating in the textile. On the other hand, Biotechnologists have set and are still developing new techniques for adequately incorporating the antimicrobial agents in the material. The JIS L 1920 test method is designed to test antimicrobial activity and efficacy on textile products. Whether you want to protect your perfect biker jacket, or old shawls, all can be tested under this method.
The fabric has a thread that weaves the antimicrobial agents into it. Some antimicrobial agents are applied to the surface of the fabric in the form of a liquid solution. Then an examination is necessary to ensure their performance.
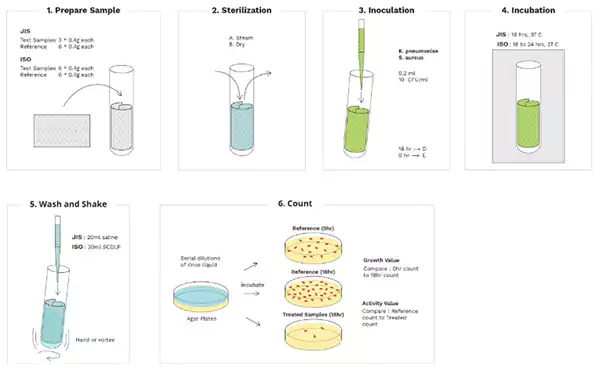
The standard JIS L 1902 test method includes three steps of examination. Let’s understand each of the steps below.
It includes the Halo method, which is quite similar to the zone inhibition technique. The zone inhibition technique is routinely used in laboratories to study the antimicrobial activity of antibiotics against particular organisms.
First, the inoculum of the test microbe is carefully poured into the molten agar before adding the test piece. Then as the agar medium and inoculum solidify, the microbiologist or biotechnologists add a piece of fabric to it and then place it for incubation. After inhibition, another task is observing and analyzing inhibition. These are basic follow-up steps of the Halo method.
The next is the absorption method for the quantitative analysis of the textile. This method is similar to the technique in another popular way for fabric analysis. The absorption method directly inoculates the bacterial sample onto the finished textile sample. Alternatively, the colony plate count method or the adenosine triphosphate luminescence methods are also used for quantitative analysis of textile products for antimicrobial activities.
The microorganism plays a vital role in the deterioration of any material that comes into contact with the microbial suspension. When The fabric and finished textiles products connect with the body, they become more prone to the attack of various types of microorganisms. The fabric is more prone to microbes because of sweat from the person’s body.
To get good quality and aesthetic value, it becomes essential to incorporate antimicrobial agents into the fabric. The JIS L 1902 test method helps determine or test the proper incorporation of the antimicrobial agents into the material. This is essential for assessing the quality of the textile.
Here is the procedure for testing the JIS L method is listed below:
The first step is the preparation of the inoculum of the microorganism by growth in the culture medium. Usually, the laboratories perform tests for Staphylococcus, Klebsiella pneumonia, and Escherichia coli. Though if you want, the laboratory can perform the test for another microbe also.
The sample of the fabric is first placed in the test tube and sterilized. Then they take two samples, one as reference or control and another one as the test sample. Sterilization with the steam method using an autoclave or the dry method using the microbial oven.
After the sample sterilization, technicians inoculate microbes with the help of the dropper. While doing this, they take special care to ensure that the inoculum of the microbes is only in contact with the fabric.
Then they determine initial concentrations of the microorganism at the time to zero by the elution method. The next step is the dilution of samples and plating of the control fabrics. The control is run along with the test samples to ensure that the technique efficiently neutralizes the antimicrobial agents.
Once the injection of the microbes is complete, they are kept for incubation at body temperature at 37 C for 18 hours. In this period, the growth of the microorganism occurs.
Now add saline to the test tube, and dilute the microbial counts. Again, the diluted samples are poured on the agar plate, and the count of the microbes is determined.
There is a reduction of the microorganisms compared to the control sample and the time zero model observed.
With the growing demand for the antimicrobial activity of fabrics and textile products, it has become essential to test their antimicrobial activities. JIS L 1902 test method is one of the effective methods for the examination of antimicrobial activity. Various laboratories around the world have adopted the techniques of textile antimicrobial testing. You can easily find microbial laboratories having such testing in your city too.
