According to a recent report from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the US core PPI fell to 3.4%, lower than expected, signifying that inflation might be cooling and marking its first decline from July. (MSN: PPI Statistics)
Do you also get confused by such news and look for concluding lines to explain what has been described in the economics jargon? If yes, then you are not the only one. These inflation measures, like the CPI, PPI, etc., can seem quite heavy and confusing, especially to those with no background knowledge of them.
But not anymore, because in this post, we will discuss everything you should know about the US core PPI, how it differs from other inflation units, its impact on crypto exchange, and economic policies.
Let’s dive right into it!
The US core PPI can be described as the combination of thousands of indexes from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) that inform about the average change over a specific period in prices of domestically produced goods and services.
In short, Core PPI monitors and tracks inflammation from the manufacturer’s perspective. It excludes the food and energy sector and hence, represents inflationary trends without the shifts or spikes caused by these highly volatile industries.
The infographics below show the US producer price index relative importance of commodities.
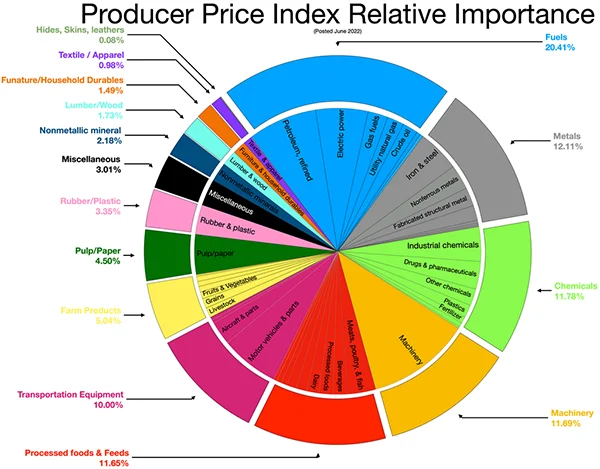
As it provides information about inflation trends and cost pressure, PPI strongly influences markets and investments. Here is how the fluctuations in PPI impact these industries:
The data-driven decisions made by investors and industry leaders help stabilize markets and maintain steady economic growth.
While there are several inflation measures, Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index PPI are the most well-known indicators of inflation. Here is a comprehensive comparison of the two:
| CPI | PPI |
| The CPI is the measure of fluctuations observed in the average consumer goods prices over time. | The PPI is the measure of pricing changes and inflation from the manufacturing end. |
| Rising prices represent that the economy is booming, while deflating prices signify a slowing economy. | Higher PPI means an increase in consumer prices and vice versa. |
| CPI is used by investors to determine the state of the Federal Reserve, whether it is likely to raise, lower, or remain steady. | PPI helps investors predict the consumer price changes that might be observed in the months ahead. It is an extremely useful tool for investors to forecast the inflationary environment. |
Apart from these two,
The change in prices at the producer level has a significant influence on the whole market. Because the US Core PPI measures inflation at a wholesale level, it proved to be extremely useful for policymakers, specifically in the Federal Reserve.
An increase in PPI indicates inflation risks and signals authorities to spike interest rates to stabilize the market. On the other hand, declining core PPI signifies declining demand and highlights the need for more accommodative policies.
Additionally, the core PPI, along with some other economic indicators, can help forex traders predict changes in exchange rates and make better judgments.
TRIVIA
The 1970s are the most well-known period of lasting inflation, caused by two oil supply-related issues. Oil prices also spurred inflation in the late 1980s and early 1990s, but it wasn’t much of a concern in the US again until 2022.
As we established in this article, the Core PPI holds great significance for traders, investors, and industry leaders. Since the Core PPI excludes the highly volatile food and energy prices, it gives a clear picture of the long-term inflation trends.
This serves as an early indicator of the inflationary patterns and shapes interest rates, policies, and economic forecasts. In the end, we can say that businesses can use the Core PPI data as a guide to analyze market trends and plan for future costs.
