The consumer goods industry is an important part of the U.S. economy. According to the National Retail Federation, retail sales accounted for $5,570.4B in 2020, making up a sizeable chunk of GDP and total employment. This shows how much this sector contributes to economic activity in the U.S. In recent years, retail sales growth in person has been modest to a weak global economy and increasing competition from e-commerce sites like Amazon and Walmart.
An official Press Release from the United States Census Bureau (January 13, 2022) provides clear insights into the state of the U.S. Retail Sales industry:
According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2020 Annual retail trade survey (ARTS), national retail sales increased by 3.1% to $5,402.3B in 2019, to $5,570.4B in 2020.
In 2020, electronic shopping and mail-order houses (NAICS4541) had $888.5B in sales, an increase of 35.2% over 2019. This was the biggest year-to-year growth of any industry in 2020.
Additional highlights from the retail sales sector:
However, there are signs that negative trends may be reversing with retail sales of 4-5% during 2021 despite the pandemic. The demand for essential items such as groceries has increased significantly due to stay-at-home orders leading consumers to buy more online than ever before. This shift towards online shopping is growing steadily as many consumers have become accustomed to buying things online or through delivery apps instead of going into stores.
The introduction of remote work has affected the retail sales market in a few ways. Firstly, it has caused many people to shop online and through delivery services more than before due to public health concerns and social distancing measures during the pandemic. Moreover, this shift toward digital shopping will continue indefinitely. As a result, many consumers have become accustomed to buying things online or through delivery apps instead of going into stores themselves.
For those who must go out and shop in person, there is now a greater emphasis on safety protocols in-store via contactless payments and curbside pickup options, which retailers have rapidly adopted since the start of the pandemic. These entrenched offerings make it easier for customers to purchase items without risking their safety while also increasing convenience when shopping at brick-and-mortar stores. These changes are here to stay due to customer demand for these services.
Remote work has also created fantastic opportunities for retailers as more people look for home office furniture and other products needed to create comfortable workspaces within their homes. In addition, with more people spending time indoors, they are looking for recreational activities like gaming consoles or streaming devices that they can use while staying at home, which further increases revenue potentials within this sector from increased consumer demand stemming from remote work situations.
The stay-at-home orders implemented across the U.S. during 2020 and 2021 profoundly affected how consumers shop and interact with retail establishments. While online shopping has dramatically increased as more people turn to e-commerce sites like Amazon and Walmart, many in-person shopping centers are rapidly declining.
This is not only due to the decrease in foot traffic but also the psychological shift of consumers (some may no longer feel comfortable or safe going into physical stores). This has been exacerbated by sky-high inflationary pressures which are clipping retail purchases at more expensive physical locations.
From an economic standpoint, this shift away from traditional malls could be devastating for local economies that rely heavily on sales tax revenue from these stores. Retailers in strip malls may find it easier to survive with customers visiting their businesses in person. Many retailers have already gone out of business since e-Commerce giants took over, and this trend is likely to continue for a variety of reasons.
In addition, a psychological impact is associated with this shift away from traditional malls and toward online shopping, which can lead to feelings of isolation and disconnection from society. Consumers now must rely solely on digital platforms for social interaction, which can leave them feeling disconnected from their communities and unable to connect with others physically in public spaces such as mall walkways or store aisles.
Overall, the decline of physical retail stores caused by stay-at-home orders, a rise in remote work, and the convenience of e-Commerce have had economic and psychological effects on American consumers. The new normal is shaping how customers view shopping experiences now and in the future. It remains unclear what will become of traditional in-person malls, but one thing is sure: shoppers will never experience them quite like before.
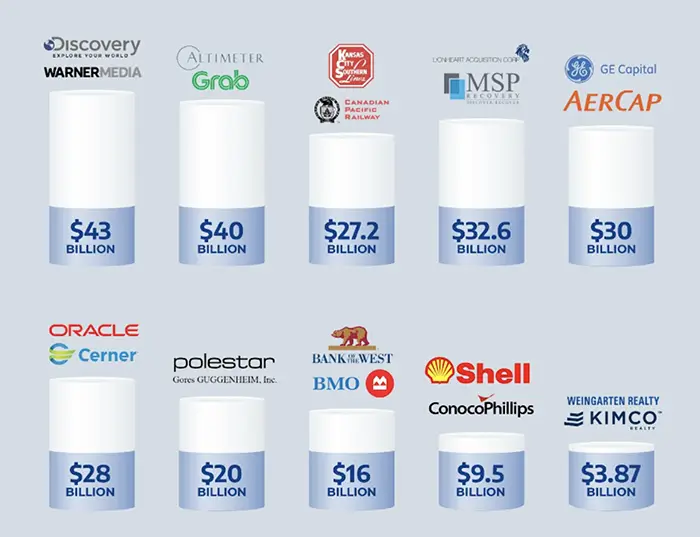
Another factor affecting growth in the consumer goods industry is mergers and acquisitions (M&A). An M&A occurs when two companies combine their assets and operations to create synergy, which could result in higher profits or greater market power than if they were separate entities. In recent years, hundreds of notable M&As have been announced by players within the consumer goods industry. These include the following deals:
These deals provide opportunities for new products or services while also helping companies expand their reach into new markets, which can help foster innovation and further boost economic activity throughout the nation’s economy.
Automation has significantly impacted productivity gains within businesses within this sector. But the impacts are felt far and wide. There have also been significant job losses among unskilled manual laborers who can no longer compete against machines. Remember, machines do not require breaks or rest periods like humans do when performing specific tasks. For example, human workers require rest periods during the day while stocking shelves or bagging items at checkout counters.
Automation has had mixed effects on workers depending on their skill set. Workers without specialized training have been displaced from jobs, while others with higher levels of education have seen wages rise due to increased efficiency gained from these automated systems. Ultimately, we need government policies that support retraining programs so those who lost jobs can find ones suited for them again. This can be possible given all the changes happening across various sectors due to advancements made by automation technology.
Overall, it’s clear why the Consumer Goods Industry plays an essential role in U.S. economic activity both now and into the future long after recent pandemic-related events. This industry accounts for a large portion of the Gross Domestic Product held steady throughout tumultuous times while continuing to fuel innovation through Mergers & Acquisitions activities.
Plus, the Consumer Goods Industry provides an opportunity via automation technology advancement that wasn’t there before, allowing us to develop better ways of doing things faster. This new U.S. industry can improve competitiveness internationally compared to other nations around the world.
