
Bitcoin and related distributed ledger technologies have become a very hot topic recently. Many industries are currently exploring new possibilities and use cases for emerging blockchain technology every day.
The invention of Bitcoin and blockchain technology has brought in a huge change across many industries, and intellectual property transactions are not any different.
But how can we use blockchain technologies within the context of intellectual property (IP)?
In this article, we will talk about Bitcoin features, what is the core technology behind it and how it plays a major role in the field of intellectual property.
Bitcoin is a new-age type of digital currency also known today as a cryptocurrency. It can be traded in exchange for goods and services. It is a non-fungible currency that falls outside the purview of the banks or any of the world’s governments.
There are various benefits of Bitcoin as any of its holders can buy, sell, and exchange goods or services without the need to go through any central authority, bank, or government acting as a middleman.
Bitcoin transactions are usually made by digitally exchanging anonymous and heavily encoded data via a peer-to-peer or P2P network.
FUN FACTS
Bitcoin has a maximum market cap of 21 million coins. So, if all coins were distributed to the population equally, each person would receive around ~0.0027 BTC.
Bitcoin was initially built with distributed and decentralized digital records in mind. This digital ledger is also known as the blockchain to keep Bitcoin safe.
Blockchain is a type of public digital ledger system that is used for recording transactions and other related data in multiple systems or computers at the same time. Blocks in a blockchain consist of units that can contain data about every transaction, including value, time, date, buyer and seller information as well as an identifying code also known as hash for each exchange.
It is designed to make it pretty much impossible to hack the system or forge the data stored on it, thereby making it a very secure, unchangeable, and tamper-proof distributed ledger.
Each system on the blockchain has a copy of the digital ledger to prevent single points of failure. If even one block has been changed or tampered with, then all other consecutive blocks in the chain must be changed in order to validate the one change that has been made.
Also, the identifying codes or the hash produced at the beginning of the transaction make it nearly impossible to fraudulently produce any new blocks or alter any existing ones.
Due to the rise of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has seen a significantly high rate of adaptation across various industries.
Blockchain specifically works as a decentralized digital form of ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and unchangeable form. This decentralization allows secure and efficient data sharing and automated processes through smart contracts.
The popularity and the high rate of adaptation of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have made it possible for digital ledger technologies to be used for management and the use of smart contracts in intellectual property management.
Intellectual property is a type of intangible property that usually includes creations of the human imagination and intellect. Anything unique your mind can create, i.e. invention, literary and artistic works, designs, symbols, names, or images that can be used in a commercial stage can be said to be a part of your intellectual property.
Within the context of intellectual property management, blockchain technology can offer benefits similar to its cryptocurrency counterparts. It can give the same enhanced security, transparency, unchangeability, and other added features with some additions to the smart contracts.
It can also streamline the intellectual property management process, facilitate transactions between parties, etc. As intellectual properties such as patents, trademarks, and art are becoming more expensive and complex to manage, the use of blockchain technology is sure to revolutionize how it is managed in the future.
Blockchain can ensure that any of its data has not been tampered with, it holds a kind of allure for various forms of intellectual property management.
It can provide increased efficiency, and authenticity in establishing ownership rights, reducing copied or counterfeit works from being published as well as licensing through smart contracts, and registering and protecting trademarks.
Within this evolving landscape, it becomes imperative to experience granimator’s edge. As IP rights, patents, and licensing agreements consider embracing Bitcoin as a medium of exchange, Granimator provides theanalytical might to navigate the crypto markets intricacies.
Through its predictive insightsand rapid data analysis, granimator ensures that stakeholders in the IP realm are always a step ahead, optimizing their financial strategies in real-time.
Any individual person who endeavors the path of an artist spends their labor, time, and money on their respective works and they want to protect what is theirs and get their fair share for their hard-earned works.
The digital ledger system used in Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency gives a person the ability to mint, set parameters, and trade their intellectual property within the blockchain.
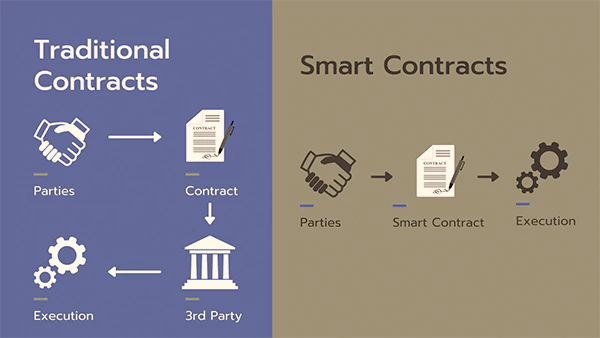
The very idea of licensing and trademarking a piece of work through the blockchain is very appealing and lucrative. It eliminates the need for any third-party involvement or any other secondary support.
Since any human intervention is removed from the equation when creating smart contracts, the code within the block automatically controls all transactions as stated within the contracts without fail.
It also makes sure that licensing and royalty payments are automated such that creators may receive their fair share of their work every time.
Like many luxury brands that see knock-offs of their brand items being sold everywhere, it is usually very hard to stop people from cloning your works digitally.
To solve this problem within the blockchain, smart contracts come with protection clauses to obstruct the sale and purchase of any cloned copy of the original minted work.
Since each work uploaded within the digital ledger is identified by a unique identifier, a consumer can ideally scan this to trace the origins of the works as well as verify its authenticity.
As more and more industries continue to rely on Bitcoin’s blockchain technology, Intellectual Property laws have to evolve in order to address the legal issues that may arise from the new language of authentication and verification process.
Bitcoin’s blockchain has the potential to streamline any future intellectual property transactions in copyright trademark and patent processes.
