As per my personal experience, Starlink is a great option for anyone who suffers from a spotty internet connection. Compared with a traditional broadband connection, Starlink is a much better and more modern option.
However, my experience with Starlink is not all heaven. There are some situations when I had to suffer from inappropriate network speed. Can bad weather be the reason for slow speed?
As Starlink is continuously collaborating with NASA and making new achievements day-by-day, its service on the Earth is often questioned. So, I decided to share my personal review and uncover whether Starlink gives good performance even in bad weather.
To find out, keep reading.
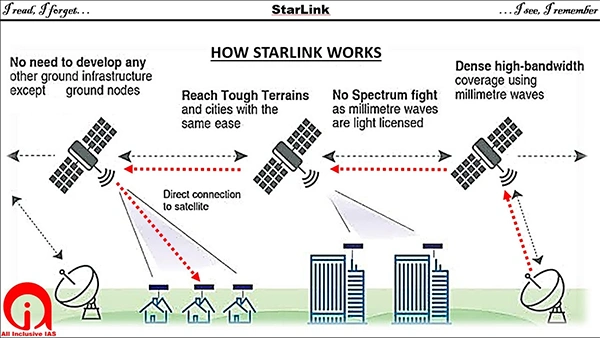
Before we dive into how Starlink actually works in bad weather conditions, it’s crucial to understand the basics of how it functions.
Starlink is a satellite-based internet service that uses a constellation of small, low Earth orbit satellites to beam internet coverage to users on the ground. When compared to the traditional geostationary satellites, which orbit around 22,000 miles, these satellites orbit much closer to Earth, and that is just about 340 miles.
Users access the Starlink network via a satellite dish, often referred to as a “Dishy,” installed at their location. The dish communicates with the Starlink satellites overhead, transmitting data to and from the users’ devices.
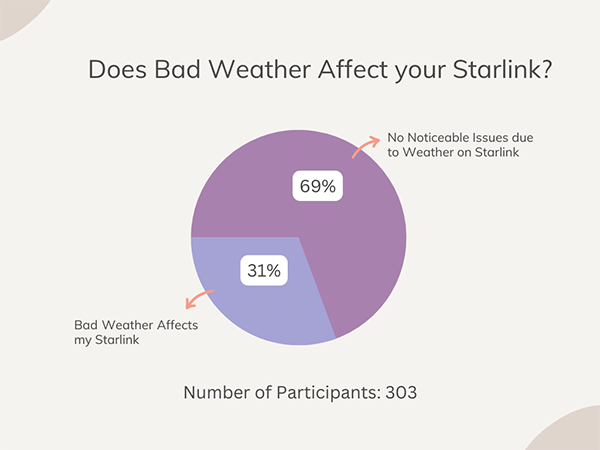
A major concern for potential Starlink users is the impact of weather on service performance. Since Starlink relies on satellites, it’s natural to wonder if severe weather conditions, such as rain, snow, or wind, could disrupt the service.
And, after all, the weather has always been a significant factor in satellite communication, influencing television and other satellite-based services. So, does Starlink work in bad weather?
So, the short answer to that question would be yes Starlink can be affected by bad weather its design minimizes many common issues, and there are steps you can take to mitigate potential disruptions. Let’s look at the different types of weather and their potential impacts.
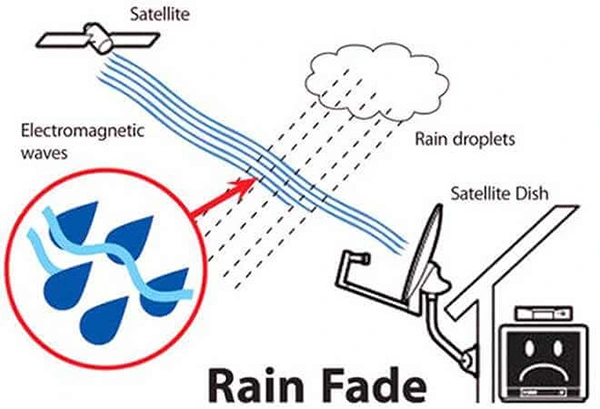
Rain is one of the most common weather conditions that could potentially affect satellite internet services. Heavy rain can cause a phenomenon known as “rain fade,” which occurs when water droplets in the atmosphere scatter or absorb the radio frequency (RF) signals used by satellites.
However, Starlink operates on the Ku and Ka bands, which are higher-frequency bands known to be more susceptible to rain fade. SpaceX has engineered the Starlink system to be resilient in most rainy conditions.
During light to moderate rainfall, most users report little to no degradation in performance. However, during extremely heavy downpours or thunderstorms, signal disruption can occur, potentially causing temporary slowdowns or outages.

Snow presents another challenge for satellite communication. When snow builds up on the Starlink dish or obstructs the line of sight to the satellites, it can cause signal degradation or even a complete loss of connectivity.
To combat this, Starlink dishes are equipped with a built-in snow-melt function. This feature heats the dish’s surface to prevent snow accumulation and ice formation, ensuring that users can maintain a clear connection even in snowy conditions.
The snow-melt feature is activated automatically when the dish detects freezing temperatures, allowing it to self-maintain without user intervention.
In general, light to moderate snow won’t pose a significant threat to Starlink’s performance. However, during heavy snowfall, signal interruptions may still occur, especially if the dish is obstructed or if snow buildup overwhelms the dish’s melting capability.
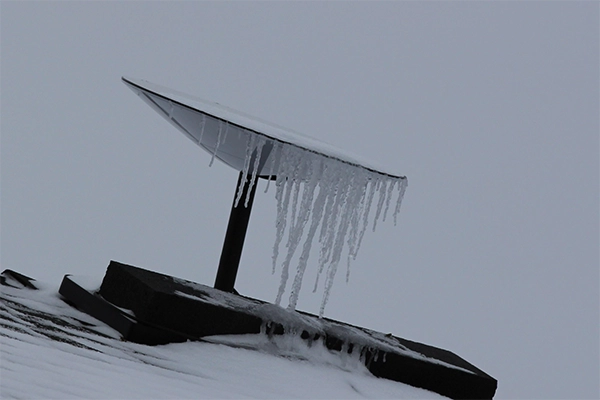

Ice is another concern, especially in regions that experience freezing rain or icy conditions. Like snow, ice can block the signal by coating the dish’s surface.
Thankfully, Starlink’s snow-melt feature also helps prevent ice from forming on the dish. When the dish detects freezing conditions, it activates its heating elements, melting ice before it becomes a significant issue.
However, extremely cold temperatures combined with freezing rain can lead to more severe icing, which may overwhelm the dish’s self-heating capabilities.

Strong winds can affect Starlink’s performance if the dish is not securely installed. Wind does not directly interfere with satellite signals, but it can cause the dish to move or become misaligned if it is not properly mounted. If the dish shifts out of alignment, it can lose its connection to the satellites, resulting in a temporary loss of service.
SpaceX recommends that users securely fasten the Starlink dish to prevent movement, especially in windy areas. The dish is designed to withstand most weather conditions, including high winds, but improper installation or mounting can still cause issues.
Fog, unlike rain, snow, or ice, typically doesn’t interfere with Starlink’s signal in any significant way. Fog consists of very fine water droplets, which generally don’t absorb or scatter the radio frequencies used by Starlink’s satellites. Users in foggy areas report minimal to no disruptions, even during dense fog conditions.
In some extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or severe storms, Starlink may experience disruptions. While the satellites themselves remain unaffected by such events, the ground infrastructure—such as the Starlink dish or power supply—can be damaged or interrupted.
Additionally, severe cloud cover and atmospheric disturbances can temporarily block the signal, leading to outages.
Do You Know?
As of September 2024, Starlink has almost 7,000 satellites in orbit and has reached a 4 million subscriber base.
While bad weather can affect Starlink’s performance, there are several steps users can take to minimize potential disruptions:
So, does Starlink work in bad weather? The answer is yes but with some caveats. However, Starlink’s advanced engineering, such as its built-in snow-melt feature, helps mitigate many of these issues, making it more resilient than traditional satellite services.
So, if you live in an area that is prone to severe weather, taking proactive measures that are mentioned in this article can help you minimize the weather impacts and maintain a stable internet connection.
