As someone who’s worked in cybersecurity, I understand how hard it is to keep sensitive data secure in a world of hackers and malware. So, what’s the best way to tackle it? It’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-171 R3.
According to some statistics, most companies that fall victim to cyberattacks (43%) are small businesses. This results in business going out of the market in under 6 months. This is concerning as you can be the next potential victim.
However, there is a framework that you could use that will better your cybersecurity. In this article, I’ll discuss 5 strategies to strengthen your cybersecurity posture with NIST 800-171 R3. So if you wish to increase your safety, read this article until the end.
The first thing that you have to do is understand all types of risks that you might face. If we talk annually, over 60% of organizations suffer from data breaches, this is why risk management is important.
Start by figuring out what are your most sensitive data. After that, map different risks against NIST 800-171 R3. You should check if your old system is creating any loopholes. Fix them immediately to avoid any invasion.
Check if your security system is lacking any type of encryption and who has access to important files. Keep in mind that the defense strategy is proactive, not reactive.
Tell me one thing, does everyone know the password to your socials? I don’t think so, it is a private thing, right? One of the most effective strategies is you limit eligibility to who can see or access the data.
You might not know, but over 95% of security breaches are done because of human error. Incorporate multifactor authentication (MFA) and only give access to the files that employees genuinely need. NIST 800-171 R3 says that access management keeps threats out of reach.
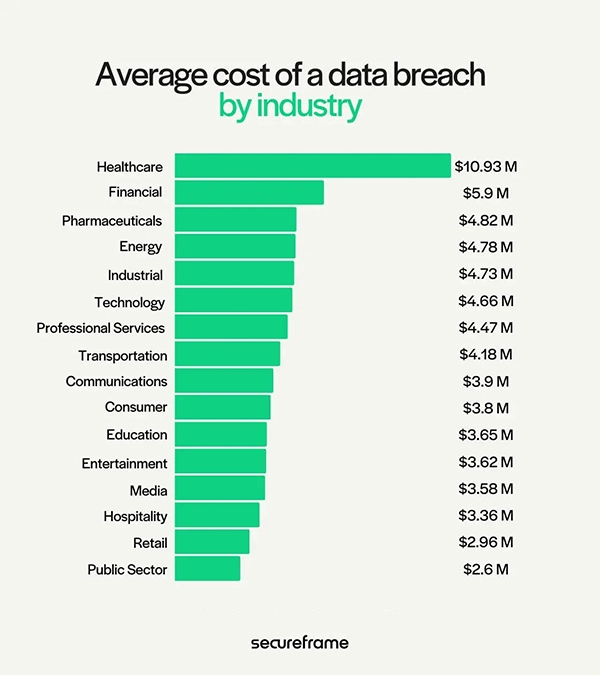
Have you wondered industry-wise how much it costs if someone breaches your data? Take a look at the graph below.
Let me clear one thing, hackers and malware aren’t the only ones who can try to steal your data. In many cases, it is an inside job. You have to keep things private and confidential and think twice before trusting someone new.
According to NIST 800-171 R3, implementing measures like end-to-end encryption must be followed by regular checks and data backup. In case, if someone does encrypt your data, they won’t be able to use it if you’ve taken this measure.
As for backups, in case you are attacked by any ransomware that can potentially lead to loss of data, you can easily recover it.

I think of my organization as it is a digital fortress, which means I have to protect it against the enemy no matter what. I start with installing firewalls, regular software updates, and threat detection systems.
Another thing that I do is isolate critical and sensitive data, as it reduces the risks of a single breach compromising everything. But how does NIST 800-171 R3 help? It gives you a blueprint of how you can build these defenses step by step, making sure there are no cracks left.
You might think that you have created the best cybersecurity program and now no one can do anything, but this would be your biggest mistake. Hackers always come up with new strategies, and you have to make sure that no matter what they do, you can safeguard your organization.
Educating your employees on cybersecurity, regular system checkups, software updates, and routine audits are just some of the many crucial things that you’ll have to adapt. You can’t afford to leave any room for mistakes.
NIST 800-171 R3 makes sure of continuous improvement. If you could follow its policies properly, you’ll always stay ahead of all the risks.
DID YOU KNOW?
In 2013 there was a data breach at Yahoo which resulted in leaked information of over 3 million users!
Hey there, seems like you’ve reached the end of this article. So, I told you bout 5 strategies that can strengthen your cybersecurity with NIST 800-171 R3. But are these five strategies enough?
The answer is no. There are more factors that you have to keep in consideration and for that, you need to have deep knowledge of NIST and its policies. You can get help from third parties who are certified in these sectors.
Let me repeat this, you can’t leave any loopholes because one mistake can take down your whole organization.
