Many customers nowadays have poor knowledge of money. Indeed, a lack of financial knowledge may be one of the reasons why many Americans struggle with saving, investing, and more often looking for a credit repair service company.
People cannot rely on one-time windfalls like the $1,400 stimulus payments provided as part of the American Rescue Plan for long-term financial planning. Individuals must instead strengthen their financial understanding to handle their day-to-day financial life while also looking forward.
Financial literacy is the collection of knowledge about money, credit, and debt management needed to live financially responsible lives. Paying off debt, making a budget, and recognizing the differences between different financial products are all examples of financial literacy. To summarize, financial literacy has a tangible influence on families as they attempt to manage their budgets, purchase a house, support their children’s education, or plan for retirement. In fact, there are many financial literacy courses as well, to help people understand it better.
People in established economies, as well as those in economically rising or developing nations, are affected by a lack of financial literacy. Nations throughout the globe are dealing with customers who do not comprehend financial principles, from Brazil to Bulgaria to India.
Though financial literacy varies by education and wealth, research reveals that highly educated clients with high salaries may be just as uninformed about financial issues as less-educated, lower-income customers.
At the same time, many individuals experience worry when they think about their own money. According to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, picking the correct investment for a retirement savings plan is more stressful than going to the dentist (OECD).
Financial literacy is essential for managing these elements, from day-to-day spending to long-term budget projections. As previously said, it is critical to plan for and save enough for suitable retirement income while avoiding excessive amounts of debt that may result in bankruptcy, defaults, and foreclosures.
Nonetheless, the United States Federal Reserve System Board of Governors discovered that many Americans are unprepared for retirement in its study, Economic Well-Being of U.S. Households in 2020. More than one-fourth said they had no retirement funds, and less than four in ten said their retirement savings are on pace. More than 60% of people with self-directed retirement funds reported having poor confidence in making retirement choices.
According to a TIAA Institute study, low financial literacy has left millennials—the greatest percentage of the American workforce—unprepared for a major financial disaster. Even among individuals who claim to be well-versed in personal finance, just 19% correctly answered questions regarding basic financial principles; 43 percent have used costly alternative financial services such as payday loans and pawnshops.
More than half do not have a three-month emergency fund, and 37% are financially vulnerable (defined as being unable or unlikely to come up with $2,000 in a month in the case of an emergency). A study from the Investor Education Foundation also confirms these data and contains surveys among men and women about financial literacy.
Financial decision-making is expected to become more onerous for consumers, compounding the challenges associated with financial illiteracy. Four themes are combined to highlight the necessity of making careful and educated financial choices.
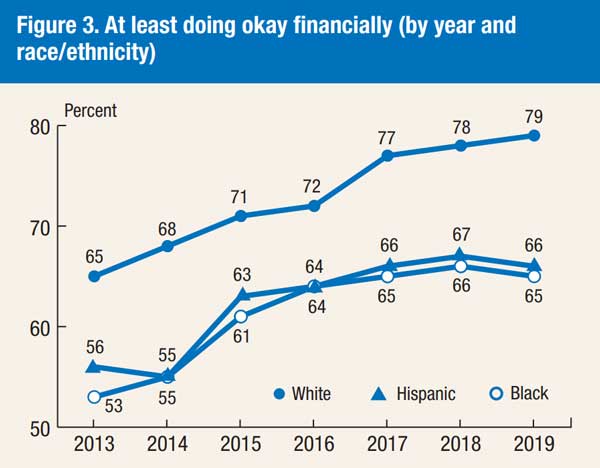
The playing ground is far from equal when it comes to financial literacy. Despite the last decade’s economic development and improving employment, the FINRA research indicated that the gap between haves and have-nots may be expanding. The research also found discrepancies across ethnic groupings, with White and Asian individuals doing better than Black and Hispanic survey respondents.
White and Asian people correctly answered 3.2 of the six questions in the research. Hispanic individuals properly answered 2.6 of the six questions, whereas Black adults correctly answered 2.3.
This gap is also seen among younger individuals. According to a 2018 PISA survey, White and Asian 15-year-olds scored better on financial literacy than the total U.S. average of pupils evaluated. Hispanic and Black children, on the other hand, scored much lower.
Retirement planning is one illustration of the growing responsibility that Americans must bear for their own financial security. Past generations relied on business pension plans, now known as defined-benefit plans, to finance the majority of their retirement.
These professional-managed pension funds imposed a financial burden on the firms or governments that supported them. Consumers were not engaged in decision-making, seldom contributed to their own funds, and were unaware of the pension’s financing situation or investments.
Pensions are becoming more of an exception than the rule, particularly for new employees. Employees are frequently given the option of participating in 401(k) or 403(b) plans, in which they must determine how much to contribute and how to invest the money.
In previous generations, Social Security was a significant source of retirement income; however, many individuals now find the payments provided by Social Security to be insufficient. Furthermore, the Social Security Board of Trustees anticipates that the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance (OASI) Trust Fund (the source of retiree payments) would be emptied by 2033.
According to the 2022 Investopedia Financial Literacy Survey, Millennials and Gen Z will depend on 401(k)s, while Gen X and Boomers will rely on Social Security. According to the report, younger generations want to integrate cryptocurrencies into their retirement plans as well.
Consumers are increasingly being forced to pick between numerous investing and savings programs. These products are more complex than in the past, forcing customers to choose from a variety of alternatives with varied interest rates and maturities, decisions they are sometimes ill-equipped to make. These decisions may have an influence on a consumer’s capacity to purchase a house, fund a college education, or save for retirement, adding to the decision-making pressure.
The number of organizations providing goods and services might often be overwhelming. Banks, credit unions, insurance companies, credit card companies, brokerage firms, mortgage companies, investment management organizations, and other financial service providers are all competing for assets, causing customer uncertainty.
The financial environment is ever-changing. In a global marketplace, there are many more players and influencing elements. Financial markets are becoming increasingly faster and more volatile as a result of the rapidly changing environment caused by technology breakthroughs such as computerized trading. When these elements are combined, they may lead to competing viewpoints and make designing, executing, and adhering to a financial plan challenging.
